Prolog
The previous article provided details on how to migrate a MongoDB data set to Couchbase Server. This article shows you how to use the Couchbase SDK to access the data via a Java console application. Code snippets show how to connect to the Couchbase cluster, perform key/value operations, and execute secondary lookups via N1QL queries side-by-side with corresponding code to do the same with the Mongo Java SDK.
All code from this blog is available in the following Git repository: mongodb-to-couchbase.
Prerequisites
A Couchbase cluster containing the data set as per the details in the previous article.
Create an Application User
Before a client (application) can connect to the Couchbase Server cluster you need to define an application user that is used for authentication by the client. Couchbase Role-Based Access Control allows you to define users and assign appropriate roles to them. Use the web console to create an application user named mflix_client as follows.
Go to the Security section in the web console and click ADD USER:
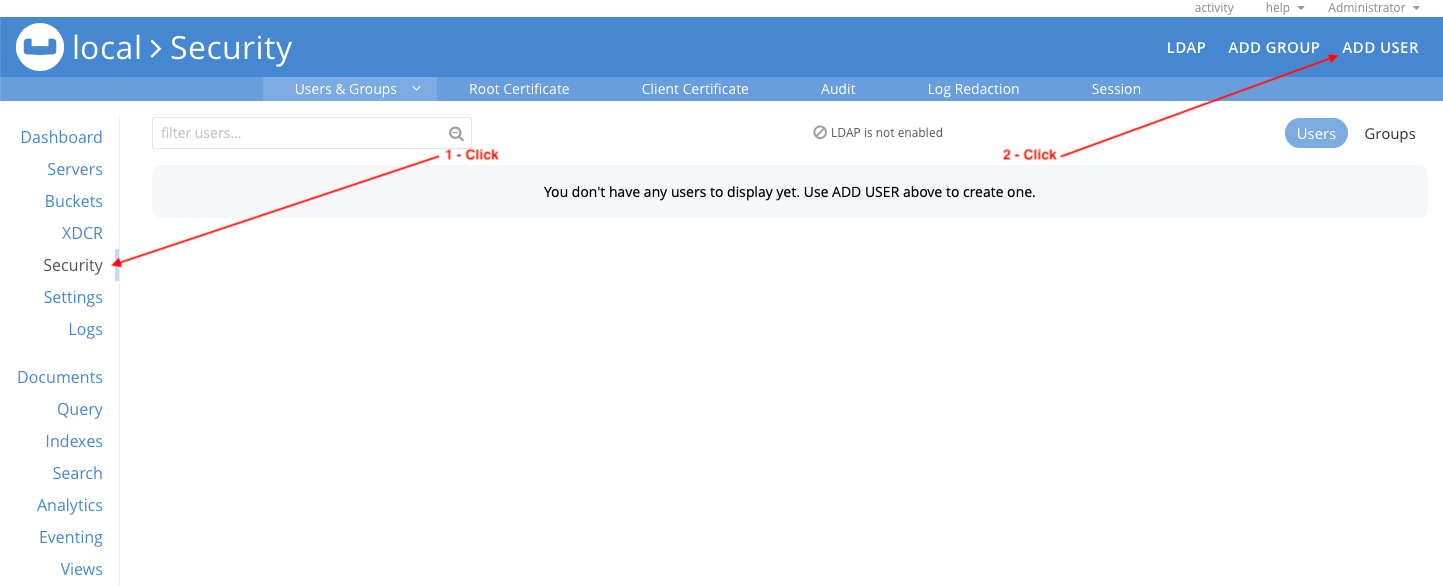
Configure the mflix_client user as follows and click Add User:
- Username: mflix_client
- Password: password (or any password of your choosing).
- Verify Password: same as Password value above.
- Roles: Expand the sample_mflix section and select Application Access. Users with the Application Access role have full read and write access to all data in the sample_mflix bucket. The role does not allow access to the Couchbase Web Console: it is intended for applications, rather than users.
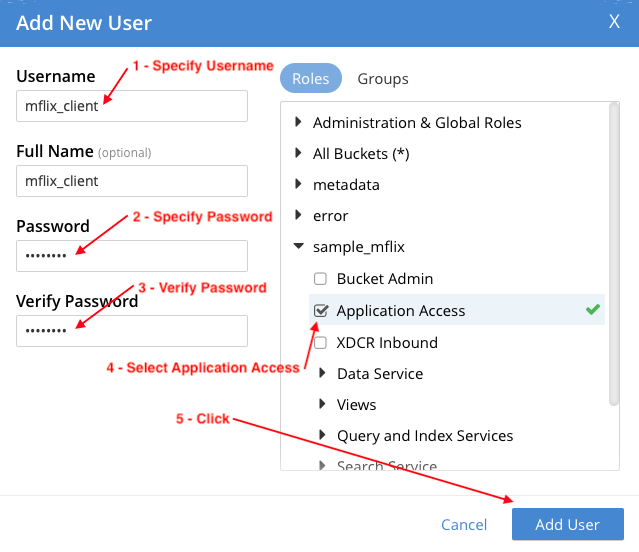
In the Security section you will see the new mflix_client user:
Create Indexes for N1QL Queries
Secondary Indexes in Couchbase Server support the efficient execution of queries (or secondary lookups) just like indexes in MongoDB. Code samples in this article execute N1QL queries that use two indexes you will create by executing N1QL queries. Go to the Query section in the web console:
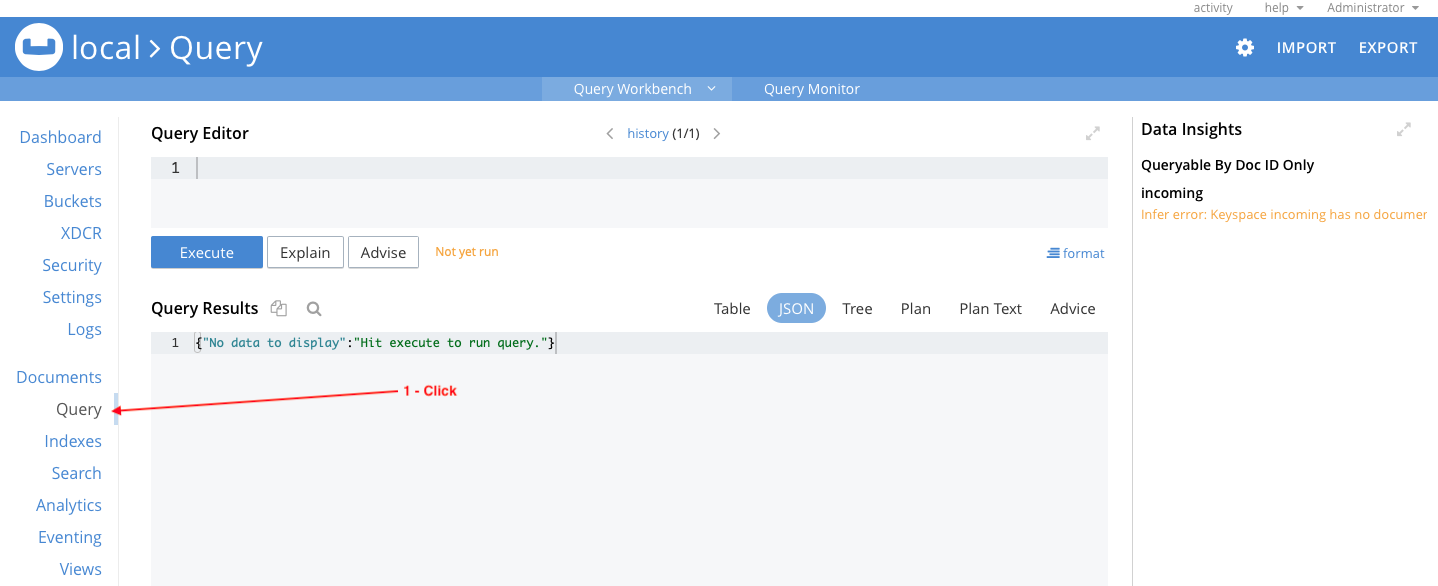
The first index is on the name attribute of all comment documents in the sample_mflix bucket. Enter the following N1QL statement in the Query Editor:
|
1 |
CREATE INDEX idx1 on sample_mflix(name) WHERE type="comment" |
Click Execute and after a few moments the index creation is complete:
The second index is on the year, imdb.rating, & title attributes of all movie documents in the sample_mflix bucket. Enter the following N1QL statement in the Query Editor:
|
1 |
CREATE INDEX idx2 on sample_mflix(year, imdb.rating, title) WHERE type="movie" |
Click Execute and after a few moments the index creation is complete:
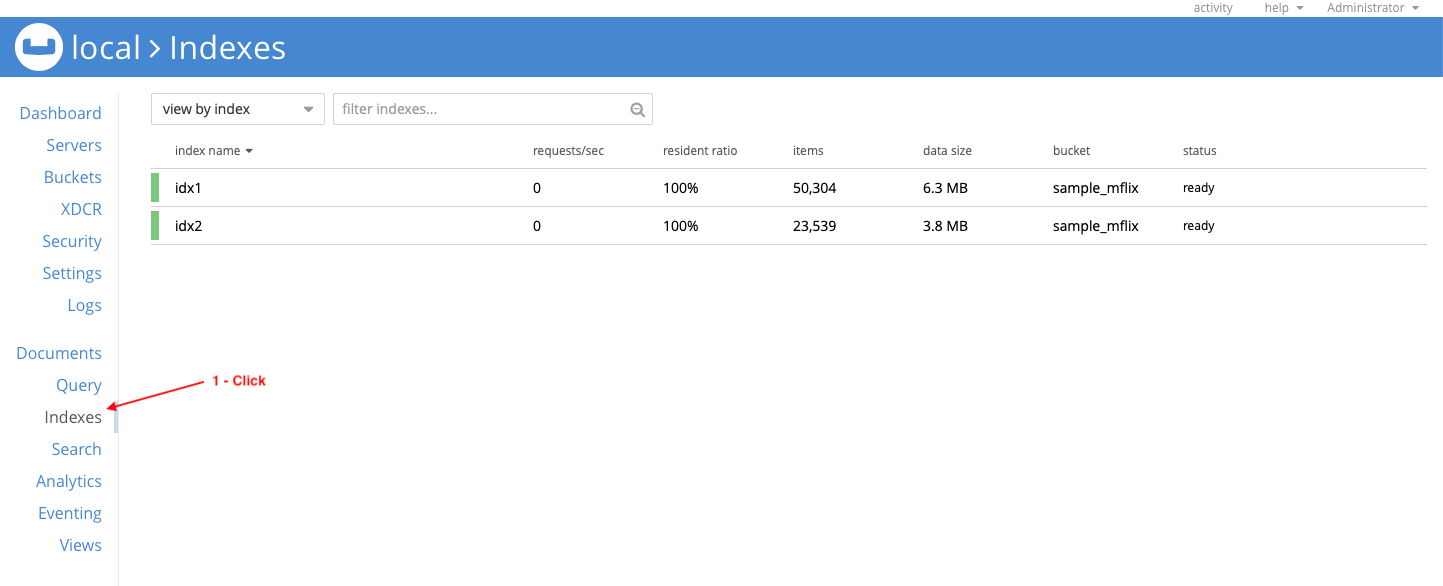
Go to the Indexes section in the web console to verify that indexes idx1 & idx2 exist:
Convert MongoDB API calls to Couchbase API calls
The sample code for this article uses the Couchbase & MongoDB Java SDKs and is provided only as an example of how to use some of the SDK APIs. Refer to the following links for the full Couchbase SDK documentation for your language:
Connect to Couchbase Server
In order to access cluster resources, clients must authenticate by passing appropriate credentials to Couchbase Server. The sample code uses the mflix_client application user credentials created above to authenticate.
The following code sample connects to the Couchbase cluster running on the specified node, gets a reference to the mflix_client bucket, and a reference to the default collection in that bucket.
Couchbase
|
1 2 3 |
Cluster cluster = Cluster.connect("127.0.0.1", "mflix_client", "password"); Bucket bucket = cluster.bucket("sample_mflix"); Collection collection = bucket.defaultCollection(); |
MongoDB
|
1 2 3 4 |
MongoClient mongoClient = MongoClients.create("mongodb+srv://<user>:<password>@<host>/<database> "); MongoDatabase mongoDatabase = mongoClient.getDatabase("sample_mflix"); MongoCollection<Document> comments = mongoDatabase.getCollection("comments"); MongoCollection<Document> movies = mongoDatabase.getCollection("movies"); |
Retrieve a Document by ID
Use the Collection.get() method to retrieve full documents by ID. The following code sample retrieves two documents from the sample_mflix bucket default collection.
Couchbase
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
// get() will throw an exception if a document with the specified ID does not exist GetResult comment = collection.get("comment:5a9427648b0beebeb69579cc"); System.out.println(comment.contentAsObject()); GetResult movie = collection.get("movie:573a1390f29313caabcd4135"); System.out.println(movie.contentAsObject()); |
MongoDB
|
1 2 |
comments.find(Filters.eq("_id", new ObjectId("5a9427648b0beebeb69579cc"))); movies.find(Filters.eq("_id", new ObjectId("573a1390f29313caabcd4135"))); |
Insert a New Document
Use the Collection.insert() method to create a new document with the specified ID & content if it does not already exist. The following code sample inserts this document in the sample_mflix bucket default collection:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
{ "name":"Anat Chase", "email":"anat_chase@fakegmail.com", "movie_id":"movie:573a1390f29313caabcd4135", "text":"This is Anat's review", "type":"comment" } |
Couchbase
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
JsonObject doc = JsonObject.create() .put("name", "Anat Chase") .put("email", "anat_chase@fakegmail.com") .put("movie_id", "movie:573a1390f29313caabcd4135") .put("text", "This is Anat's review") .put("type", "comment"); // insert() will throw an exception if a document with the specified ID already exists collection.insert("comment:5a9427648b0beebeb69579c0", doc); |
MongoDB
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Document doc = new Document("_id", new ObjectId("5a9427648b0beebeb69579c0")) .append("name", "Anat Chase") .append("email", "anat_chase@fakegmail.com") .append("movie_id", new ObjectId("573a1390f29313caabcd4135")) .append("text", "This is Anat's review"); comments.insertOne(doc); |
Insert Multiple New Documents
Batching operations allows you to make better utilization of your network and speed up your application by increasing network throughput and reducing latency. Batched operations work by pipelining requests over the network. When requests are pipelined, they are sent in one large group to the cluster. The cluster in turn pipelines responses back to the client.
The following code sample uses this approach to insert two new documents into the sample_mflix bucket.
Couchbase
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
// Create two JSON documents List<Tuple2<String, JsonObject>> documents = new ArrayList<Tuple2<String, JsonObject>>(); doc = JsonObject.create() .put("name", "Anat Chase") .put("email", "anat_chase@fakegmail.com") .put("movie_id", "movie:573a1390f29313caabcd42e8") .put("text", "This is Anat's review") .put("type", "comment"); documents.add(Tuples.of("comment:5a9427648b0beebeb69579c1", doc)); JsonObject doc2 = JsonObject.create() .put("name", "Anat Chase") .put("email", "anat_chase@fakegmail.com") .put("movie_id", "movie:573a1390f29313caabcd4323") .put("text", "This is Anat's review") .put("type", "comment"); documents.add(Tuples.of("comment:5a9427648b0beebeb69579c2", doc2)); // Insert the 2 documents in one batch, waiting until the last one is done. // insert() will throw an exception if a document with the specified ID already exists Flux .fromIterable(documents) .parallel().runOn(Schedulers.elastic()) .concatMap(doc3 -> reactiveCollection.insert(doc3.getT1(), doc3.getT2()) .onErrorResume(e -> Mono.error(new Exception(doc3.getT1(), e)))) .sequential().collectList().block(); |
MongoDB
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
List<Document> documents = new ArrayList<Document>(); Document doc1 = new Document("_id", new ObjectId("5a9427648b0beebeb69579c1")) .append("name", "Anat Chase") .append("email", "anat_chase@fakegmail.com") .append("movie_id", new ObjectId("573a1390f29313caabcd42e8")) .append("text", "This is Anat's review"); documents.add(doc1); Document doc2 = new Document("_id", new ObjectId("5a9427648b0beebeb69579c2")) .append("name", "Anat Chase") .append("email", "anat_chase@fakegmail.com") .append("movie_id", new ObjectId("573a1390f29313caabcd4323")) .append("text", "This is Anat's review"); documents.add(doc2); comments.insertMany(documents); |
Update an Existing Document
Use the Collection.replace() method to update an existing document with the specified ID only if it already exists. Couchbase supports sub-document operations which can be used to efficiently access parts of documents. Sub-document operations may be quicker and more network-efficient than full-document operations because they only transmit the accessed sections of the document over the network. Full-document and sub-document operations are atomic, allowing safe modifications to documents with built-in concurrency control.
The following code sample uses sub-document operations to update the text attribute of a specified document.
Couchbase
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
// Update a document using the sub-document API to modify the specific attribute(s) // replace() will throw an exception if a document with the specified ID does not exist collection.mutateIn( "comment:5a9427648b0beebeb69579c0", Arrays.asList(replace("text", "This is not Anat's review"))); |
MongoDB
|
1 2 3 |
comments.updateOne( Filters.eq("_id", new ObjectId("5a9427648b0beebeb69579c0")), Updates.combine(Updates.set("text", ""))); |
Update Multiple Documents
In addition to primary access via key/value APIs, you can also execute N1QL queries via N1QL APIs. N1QL is a declarative language for querying, transforming, and manipulating JSON data – think SQL for JSON.
The following code sample executes a N1QL query to update the name and email attributes for all comment documents where name is Anat Chase. This query uses the idx1 index created above.
Couchbase
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
// execute a N1QL UPDATE query via the query API String statement = "UPDATE sample_mflix " + "SET name='Anita Chase', email='anita_chase@fakegmail.com' " + "WHERE type='comment' AND name='Anat Chase'"; QueryResult updateResult = cluster.query(statement); |
MongoDB
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
comments.updateMany( Filters.eq("name", "Anat Chase"), Updates.combine( Updates.set("name", "Anita Chase"), Updates.set("email", "anita_chase@fakegmail.com"))); |
Update or Insert a Document
Use the Collection.upsert() method to insert the document if it does not exist, or replace it if it does. If a document with the specified ID does not exist, upsert() will create a new document. If a document with the specified ID exists, upsert() will update the existing document. The following code sample updates an existing document in the sample_mflix bucket.
Couchbase
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
doc = JsonObject.create() .put("name", "Mia Hannas") .put("email", "mia_hannas@fakegmail.com") .put("movie_id", "movie:573a1390f29313caabcd4135") .put("text", "This is Mia's review") .put("type", "comment"); // upsert() will update the document if it exists or insert the document if it does not exist collection.upsert("comment:5a9427648b0beebeb69579c0", doc); |
MongoDB
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
collection.replaceOne( Filters.eq("_id", new ObjectId("5a9427648b0beebeb69579c0")), new Document("name", "Mia Hannas") .append("email", "mia_hannas@fakegmail.com") .append("movie_id", new ObjectId("573a1390f29313caabcd4135")) .append("text", "This is Mia's review"), new UpdateOptions().upsert(true)); |
Delete a Document
Use the Collection.remove() method to remove a full document with the specified ID. The following code sample deletes an existing document from the sample_mflix bucket.
Couchbase
|
1 2 |
// remove() will throw an exception if the document does not exist collection.remove("comment:5a9427648b0beebeb69579c0"); |
MongoDB
|
1 |
collection.deleteOne(Filters.eq("_id", new ObjectId("5a9427648b0beebeb69579c0"))); |
Delete Multiple Documents
You can also use N1QL queries to delete documents. The following code sample executes a N1QL query to delete multiple documents from the sample_mflix bucket. All comment documents where the name is Anita Chase will be deleted. This query uses the idx1 index created above.
Couchbase
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
// execute a N1QL DELETE query via the query API String statement = "DELETE FROM sample_mflix " + "WHERE type='comment' AND name='Anita Chase'"; QueryResult deleteResult = cluster.query(statement); |
MongoDB
|
1 |
comments.deleteMany(Filters.eq("name", "Anita Chase")); |
Data Access with N1QL
N1QL can also be used to perform more complicated secondary lookups of data. The following code sample executes a blocking N1QL query to select the title, year, and imdb.rating from all movie documents where the year is between 1970 and 1979, ordered by the imdb.rating. The query uses the idx2 index created above.
Similar to batching reactive key/value operations, reactive and async querying should be used for better performance.
Couchbase
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
// execute a N1QL SELECT query (blocking) via the query API String selectStatement = "SELECT title, year, imdb.rating FROM sample_mflix " + "WHERE type='movie' AND year BETWEEN 1970 AND 1979 ORDER BY imdb.rating DESC"; final QueryResult selectResult = cluster.query(selectStatement); for (JsonObject row : selectResult.rowsAsObject()) { System.out.println(row.toString()); } |
MongoDB
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
movies.find(Filters.and(Filters.gte("year", 1970), Filters.lte("year", 1979))) .sort(Sorts.descending("imdb.rating")) .projection(Projections.fields( Projections.include("title", "year", "imdb.rating"), Projections.excludeId())); |
What’s Next
Explore the other capabilities of the Couchbase SDK including Analytics and Full Text Search. Take advantage of our free, online training available at https://learn.couchbase.com to learn more about Couchbase.
For detailed information on the architectural advantages of the Couchbase Data Platform over MongoDB see this document: Couchbase: Better Than MongoDB In Every Way.
Learn why other enterprises choose Couchbase over MongoDB: