What are data silos?
Data silos are isolated repositories of data controlled by departments or teams, often inaccessible to the rest of the organization. These silos typically arise due to a lack of communication, incompatible systems, or organizational structure. While each silo might efficiently serve its own department or team, they can lead to inefficiencies, redundancy, and missed opportunities for the rest of the company. Breaking down data silos is crucial to fostering collaboration, improving decision making, and enabling an organization to leverage its data assets fully.
This resource will explore how silos are created, dive deeper into why they’re problematic, how to spot them, and how to fix them. Keep reading to learn more.
- How are data silos created?
- Why are data silos problematic?
- How do you identify data silos?
- Examples of data silos
- How to fix data silos
- Key takeaways and resources
How are data silos created?
Before we dive into why data silos are problematic, it’s important to understand how they occur in the first place. Let’s go over some factors that contribute to silos:
- Organizational structure: The structure of an organization can lead to data silos. Departments or business units often operate autonomously, managing their data without coordination with other teams.
- Technological limitations: Some organizations use multiple databases and systems, making it difficult to integrate data across platforms.
- Company culture: Your organizational culture may contribute to data silos. Organizations that don’t encourage collaboration between teams or unintentionally stoke internal competition can lead to departmental silos.
- Lack of centralized data management tools: The absence of tools to integrate data resources can result in silos. Not using software that facilitates this can hinder data integration.
Why are data silos problematic?
Data silos can negatively impact your entire organization’s collaborative efforts, efficiency, and decision-making abilities. When organizations don’t have all the information they need (or accurate information), it creates issues that prevent teams from doing their jobs correctly. Here are some of the specific ways silos can hinder an organization:
- Data silos can lead to poor data quality. When the same data exists in different systems, it may not be consistently updated across all platforms, resulting in outdated or incorrect information.
- Data silos can cause redundancy and data duplication, wasting storage and valuable time. This issue arises when there’s a lack of integration between systems.
- Data silos lead to incomplete insights because it’s not consolidated in one system. Without a comprehensive view of all data, organizations can’t make well-informed decisions.
- Security risks are a significant concern with data silos. Managing different systems makes applying and monitoring consistent governance and security policies challenging, leading to potential vulnerabilities.
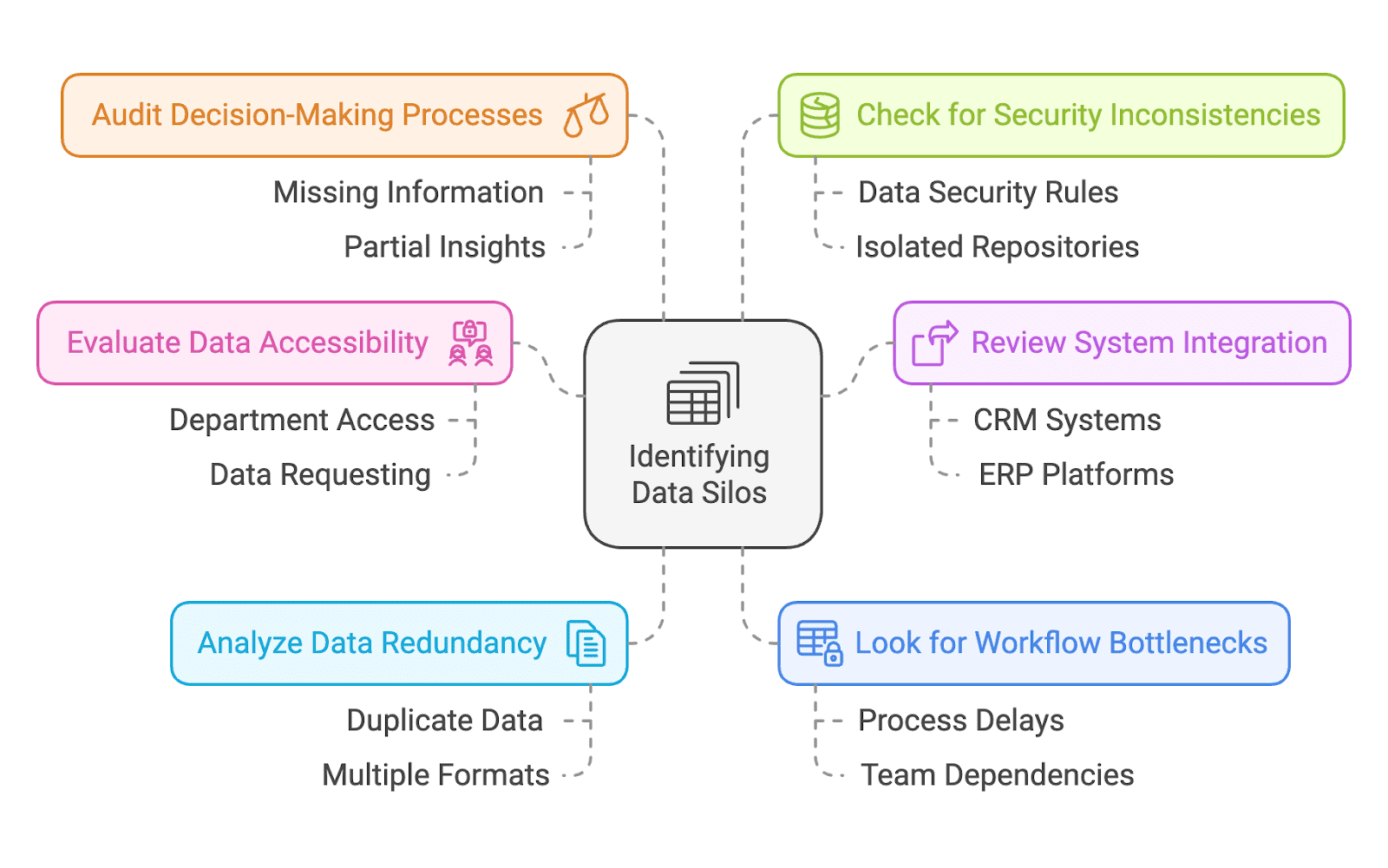
How do you identify data silos?
Identifying data silos in an organization requires careful analysis of data workflows, systems, and processes. Here are some steps you can take to identify them:
Evaluate data accessibility
Start by assessing which departments or teams have access to specific datasets. Look for situations where teams can’t easily access the data they need or situations where they need to request access from other departments to receive it. This lack of easy access can create barriers and hinder collaboration.
Review system integration
Examine whether the organization’s systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and human resources (HR) platforms, are interconnected. If systems operate independently without sharing data, they create isolated pools of information, preventing departments from collaborating effectively and accessing the full picture.
Analyze data redundancy
Check for duplicated data across platforms to ensure that the same information doesn’t exist in multiple formats or locations. Redundant data can lead to confusion, inconsistency, and inefficiencies as teams reconcile or update information in several places.
Look for workflow bottlenecks
Identify areas where processes are delayed due to a lack of data sharing between teams or systems. For example, a marketing team may need customer data but is waiting for approval from the sales team, creating a bottleneck in the workflow that slows down decision making and further action.
Audit decision-making processes
Investigate whether teams are making decisions with incomplete or fragmented data. Pay attention to complaints about “missing information” or “partial insights” during strategy discussions, as this could indicate the presence of data silos preventing a complete view.
Check for security inconsistencies
Review how data governance policies are applied across systems. Silos often emerge when different platforms have varying data security rules, leading to inconsistent handling of sensitive information and creating isolated data repositories.
Examples of data silos
In many organizations, different departments manage data independently, using their own systems tailored to their specific functions. While this might seem efficient for individual teams, it can lead to silos within an organization. Here are some examples of how these manifest:
- Geographic: Regional offices store data locally due to compliance or infrastructure limitations, preventing real-time access by the central team.
- System: Separate ERP, CRM, and HR platforms don’t share data, requiring manual reconciliation to generate reports.
- Legacy: Older on-premises systems used by specific teams are incompatible with modern cloud-based tools, restricting data flow.
How to fix data silos
Fixing data silos requires addressing both technical and organizational challenges. Here are practical steps to eliminate them:
Encourage collaboration
Foster a culture of open communication and collaboration across departments. By prioritizing transparency as a company initiative and framing data sharing as beneficial to every department, you can reduce the tendency to isolate information.
Break down technological barriers
Replace legacy systems that don’t communicate well with modern tools. Tools that support APIs and real-time data sharing can help bridge the gaps between systems. Although they can be expensive and migrating data to these systems can be complex, it’s worth the time and effort it will save in the future.
Invest in centralized data platforms
Use tools like data warehouses, data lakes, cloud platforms, or customer data platforms (CDPs) that centralize data from multiple sources. Software like this makes it easier to access, share, and analyze data that will accurately influence organizational decisions.
Standardize processes across the organization
Establish consistent protocols for collecting, storing, and managing data. Standardized processes ensure that data from different departments is compatible and can be easily integrated.
Provide data literacy training
Equip employees with the skills and knowledge they need to understand and use data effectively. By empowering teams to work with shared data, organizations can encourage cross-functional insights, ultimately leading to better information.
Audit and optimize data practices
Conduct annual reviews of how data is stored, accessed, and shared within the organization. By identifying potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies, you can take steps to improve processes and continuously eliminate factors that lead to data silos.
Key takeaways and resources
Data silos are collections of data within an organization that exist in a vacuum. They cause problems because they contribute to inefficiency, missing or inaccurate data, and security risks. To identify data silos, you should assess workflows, data accessibility, and integration abilities among existing tools. To resolve them, you should encourage sharing and collaboration between departments, invest in tools that centralize and integrate data, enforce strong data governance policies, and conduct annual audits to spot opportunities for improvement. Ultimately, enabling better collaboration leads to more informed decision making, efficiency, and security.
To learn more about data management best practices, you can review our blog and concepts hub and check out the resources below: